1. Nuclei [2][3][4]
- ProjectDiscovery에서 개발한 YAML 기반 템플릿을 사용하여 취약점을 스캔하는 go 언어 기반의 오픈소스 취약점 스캐너
> YAML 파일로 취약점 스캔 탬플릿을 정의하며, 해당 템플릿을 통해 취약점을 식별
> 템플릿은 직접 작성하거나 커뮤니티에서 제공하는 템플릿 활용 가능
- 웹 애플리케이션 취약점, 네트워크 서비스, API 스캔 등이 가능
- 멀티스레드 기반의 빠른 스캔, 유연성 및 확장성 등의 장점이 있음
2. CVE-2024-43405
- Nuclear의 템플릿 서명 검증 시스템에서 발생하는 서명 검증 우회 취약점
영향받는 버전 : Nuclei 3.0.0 ~ 3.3.2 이전 버전
- ProjectDiscovery는 무단 데이터 액세스와 시스템 손상을 방지 하기위해 서명 검증 메커니즘을 구현 (위변조 방지, 무결성 확인)
> 템플릿 파일 내용을 기준으로 SHA256을 계산해 "#digest:"로 삽입
| 서명 검증 과정 | |
| 서명 추출 | 정규식을 사용하여 "#digest:" 줄 검색 |
| 서명 제거 | 템플릿 콘텐츠에서 서명 줄 제외 |
| 해시 계산 | 서명을 제외한 콘텐츠 해시 계산 |
| 서명 검증 | 계산된 해시를 추출된 서명과 비교하여 검증 |
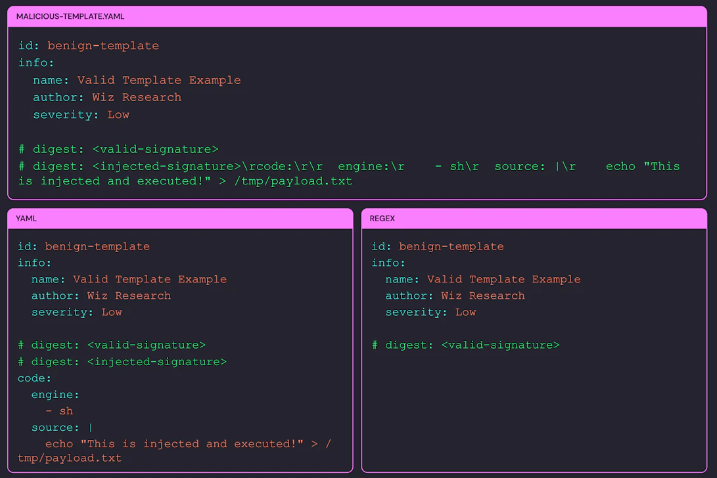
- Nuclear 서명 검증 논리에서 서명 추출 및 제거는 정규표현식을 사용하며, 이후 구문 분석 및 실행에는 YAML 파서 사용
> Line1 ~ Line31 : 첫 번째 서명을 찾아 템플릿에서 서명을 제거
> Line33 ~ Line51 : 서명 검증 후 YAML로 구문 분석 및 실행
> 첫 번째 서명(#digest:)만 확인 : 악성코드가 포함된 두 번째 서명이 검증되지 않고 템플릿에 남아있을 수 있음
> 줄 바꿈 해석 불일치 : 정규 표현식을 사용한 서명 검증과 YAML 파서 간 줄 바꿈 해석 불일치로 추가 콘텐츠를 삽입할 수 있음
| 구분 | 설명 |
| 정규 표현식 | ‘\r’를 동일한 줄의 일부로 간주 |
| YAML 파서 | ‘\r'를 줄 바꿈 문자로 해석 |
1 var (
2 ReDigest = regexp.MustCompile(`(?m)^#\sdigest:\s.+$`)
3 SignaturePattern = "# digest: "
4 )
5
6 func RemoveSignatureFromData(data []byte) []byte {
7 return bytes.Trim(ReDigest.ReplaceAll(data, []byte("")), "\n")
8 }
9
10 func (t *TemplateSigner) Verify(data []byte) (bool, error) {
11 digestData := ReDigest.Find(data)
12 if len(digestData) == 0 {
13 return false, errors.New("digest not found")
14 }
15
16 digestData = bytes.TrimSpace(bytes.TrimPrefix(digestData, []byte(SignaturePattern)))
17 digestString := strings.TrimSuffix(string(digestData), ":"+t.GetUserFragment())
18 digest, err := hex.DecodeString(digestString)
19 if err != nil {
20 return false, err
21 }
22
23 buff := bytes.NewBuffer(RemoveSignatureFromData(data))
24
25 // Verify using standard Go's ECDSA
26 if !t.verify(sha256.Sum256(buff.Bytes()), digest) {
27 return false, errors.New("signature verification failed")
28 }
29
30 return true, nil
31 }
32
33 // SecureExecute is a mock we at Wiz created that mimics Nuclei's logic to illustrate the vulnerability,
34 // verifying a template's signature, parsing it as YAML, and executing it.
35 func SecureExecute(rawTemplate []byte, verifier *TemplateSigner) (interface{}, error) {
36 // Verify the template signature
37 isVerified, err := verifier.Verify(rawTemplate)
38 if err != nil || !isVerified {
39 return nil, errors.New("template verification failed")
40 }
41
42 // Parse the template
43 template := &Template{}
44 err = yaml.Unmarshal(rawTemplate, template)
45 if err != nil {
46 return nil, errors.New("couldn't unmarshal template")
47 }
48
49 // Execute the template and return the result
50 return template.execute()
51 }
- 두 번째 서명에 '\r'를 포함한 악성코드를 삽입하여 악용 가능
> 두 번째 서명은 서명 검증 과정을 거치지 않고, YAML에서 구문 분석 후 실행됨
3. 대응방안
- Nuclei 3.3.2 이상으로 업그레이드
- 악성 템플릿의 실행을 방지하기 위해 샌드박스 또는 격리된 환경에서 Nuclei 실행
4. 참고
[1] https://www.wiz.io/blog/nuclei-signature-verification-bypass
[2] https://github.com/projectdiscovery/nuclei
[3] https://github.com/projectdiscovery/nuclei/blob/dev/README_KR.md
[4] https://bugbounty.tistory.com/55
[5] https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-43405
[6] https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/nuclei-flaw-lets-malicious-templates-bypass-signature-verification/
[7] https://thehackernews.com/2025/01/researchers-uncover-nuclei.html
[8] https://www.dailysecu.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=162701
'취약점 > By-Pass' 카테고리의 다른 글
| GitLab SAML 인증 우회 취약점 (CVE-2025-25291, CVE-2025-25292) (0) | 2025.03.22 |
|---|---|
| Fortinet 대체 경로 또는 채널을 사용한 인증 우회 취약점 (CVE-2024-55591) (1) | 2025.01.20 |
| Microsoft 다중인증 우회 취약점 (0) | 2024.12.16 |
| WordPress CleanTalk 플러그인 인증 우회 취약점 (CVE-2024-10542, CVE-2024-10781) (0) | 2024.11.27 |
| NVIDIA Base Command Manager 인증 누락 취약점 (CVE-2024-0138) (1) | 2024.11.26 |
